Brain–Computer Interfaces: Minds & Machines Connecting
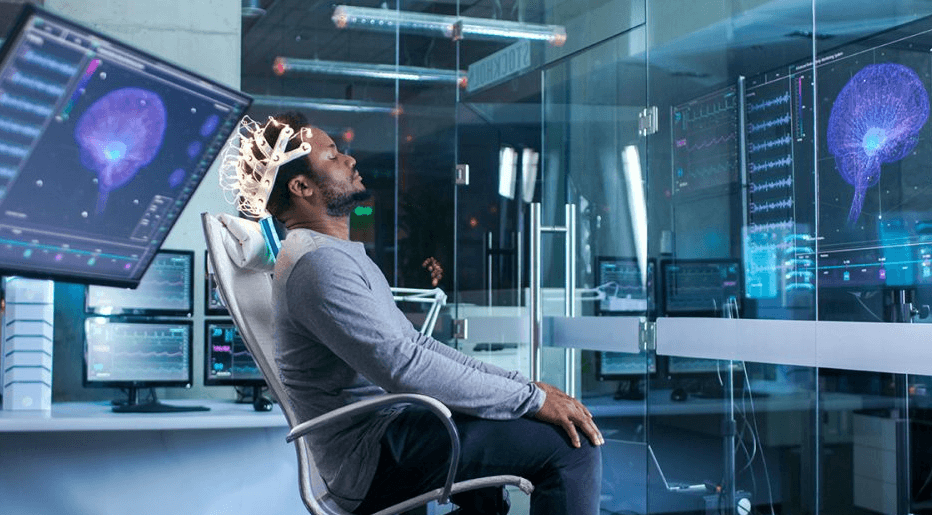
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) represent a significant advancement in technology, facilitating direct communication between the human brain and external devices. These systems leverage complex algorithms to interpret neural signals, enabling diverse applications, from medical rehabilitation to cognitive enhancement. However, the rapid development of BCIs raises critical ethical questions. Issues of privacy, consent, and equitable access necessitate thorough examination as society navigates this evolving landscape. The implications of these developments warrant careful consideration.
The Technology Behind Brain-Computer Interfaces
As brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) evolve, they leverage a combination of advanced signal processing, machine learning algorithms, and neuroimaging techniques to facilitate direct communication between the brain and external devices.
These neurotechnology advancements enhance the accuracy and efficiency of data interpretation, allowing for real-time interaction.
Signal processing techniques play a crucial role in filtering neuronal signals, thus optimizing device responsiveness and user experience.
See also: Blockchain Beyond Crypto: Real-World Use Cases in 2025
Applications and Benefits of BCIs
The advancements in brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have opened up a diverse range of applications across multiple fields, demonstrating significant potential to enhance human capabilities and improve quality of life.
Notably, BCIs facilitate medical advancements by enabling communication for individuals with disabilities and offering cognitive enhancement through neurofeedback. These innovations support rehabilitation, augment mental acuity, and promote independence, reshaping the landscape of human-machine interaction.
Ethical Considerations and Future Challenges
While brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer transformative possibilities, they also raise significant ethical considerations and future challenges that must be addressed.
Privacy concerns loom large, as the potential for unauthorized data access threatens individual autonomy.
Additionally, consent issues arise, especially regarding the capacity to grant informed consent in vulnerable populations.
Navigating these complexities is essential to ensure responsible development and implementation of BCIs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) exemplify a transformative technological advancement, with an estimated 10% of individuals with disabilities potentially benefiting from enhanced communication and mobility through these systems. However, as BCIs gain traction, addressing ethical concerns such as privacy, consent, and equitable access is imperative. The successful integration of BCIs into society hinges on responsible development and fostering public trust, ensuring that the profound benefits of this technology are accessible to all, without compromising individual rights.